Continuous Raster Data Examples
Click the Symbology tab. They are usually regularly spaced and square but they dont have to.
Introduction To Raster Data Introduction To Geospatial Concepts
Adding half a foot and describing it in a decimal format are key to this being an example of continuous data.

. A raster object can be created by calling the rast function and specifying an external image file as an argument. 21 Rainfall in the Sudan Among the most common examples of. Continuous Data Examples.
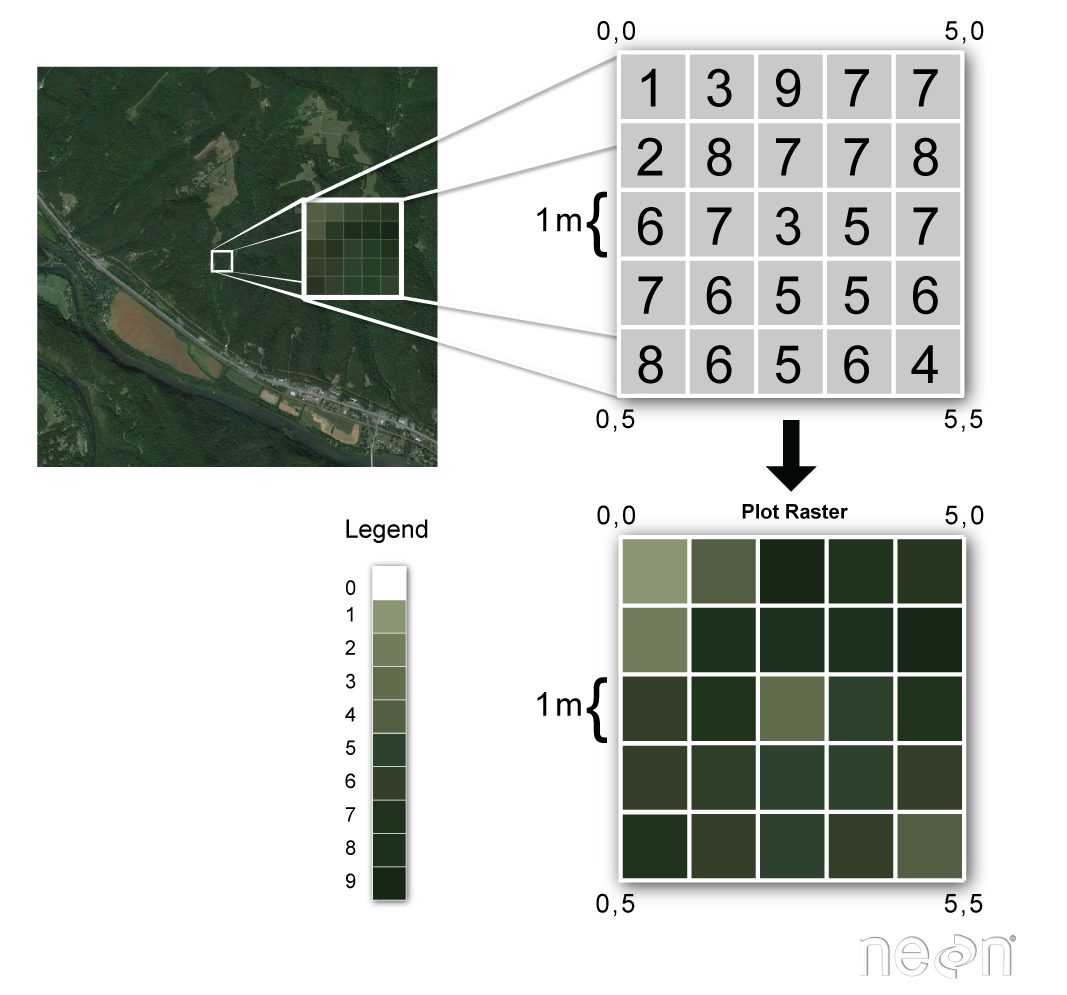
Examples of Discrete and Continuous Information. Raster data is any pixelated or gridded data where each pixel is associated with a specific geographical location. Someone can be 55 feet.
In the table of contents right-click the raster layer that you want to display across a color ramp and click Properties. Continuous data has no clearly defined boundaries. These examples is a case study in Chapter 5 of BG and the data for each example has been reconstructed in ARCMAP.
Every point on a map made with continuous GIS data will contain a value. Optionally if your raster. Elevation slope temperature and precipitation are.
Raster data can be defined as the cell-based data and it consists of aerial and View the full answer. Two common data formats based on the raster data model are grids and images. 61 Importing Raster Data.
For example in a continuous grid representing elevation one cell might store an. The value of a pixel can be continuous eg. Discrete data is adequately piece of cake to epitome and understand - nigh all vector data used in the GIS is.
Raster data is made up of pixels also referred to as grid cells. In this example a dataset of land surface.

What Is Raster Data Help Documentation

Introduction To Raster Data Introduction To Geospatial Concepts
Introduction To Raster Data Introduction To Geospatial Concepts

Lecture On Visulalization Of Raster And Vector Data I Ncsu Geospatial Modeling And Analysis Youtube
No comments for "Continuous Raster Data Examples"
Post a Comment